There are differences between pulse laser rust rem
There are differences between pulse laser rust removal machines and fiber lasers in terms of rust removal principles, application scenarios, and advantages and disadvantages.
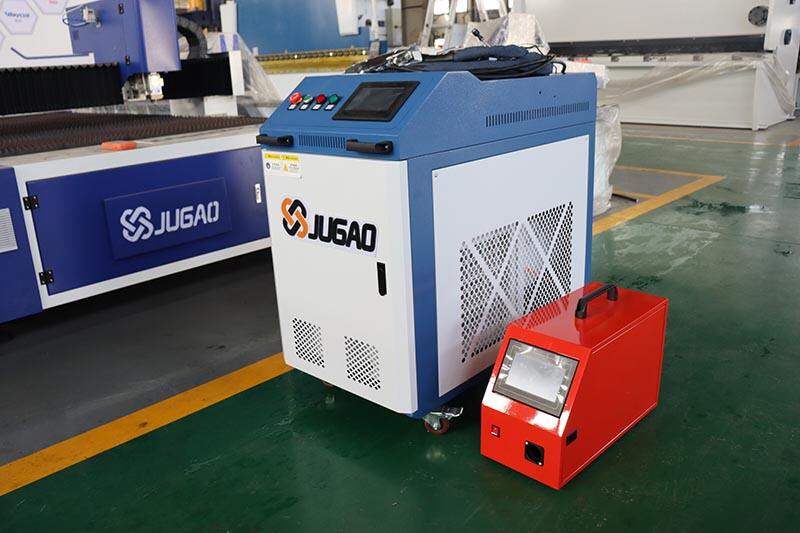

Principle of rust removal: Pulse laser rust removal machine uses the high energy density and rapid light vibration effect of pulse laser to convert the laser light energy into the heat energy of the material,generate thermal stress or shock wave to remove pollutants. The accumulated heat of this method does not exceed the melting point of the base metal, which can effectively protect the base material from damage. Fiber laser impacts the rust layer through a continuous beam, similar to high-pressure water gun rust removal, continuous impact on the rust layer to achieve the rust removal effect.
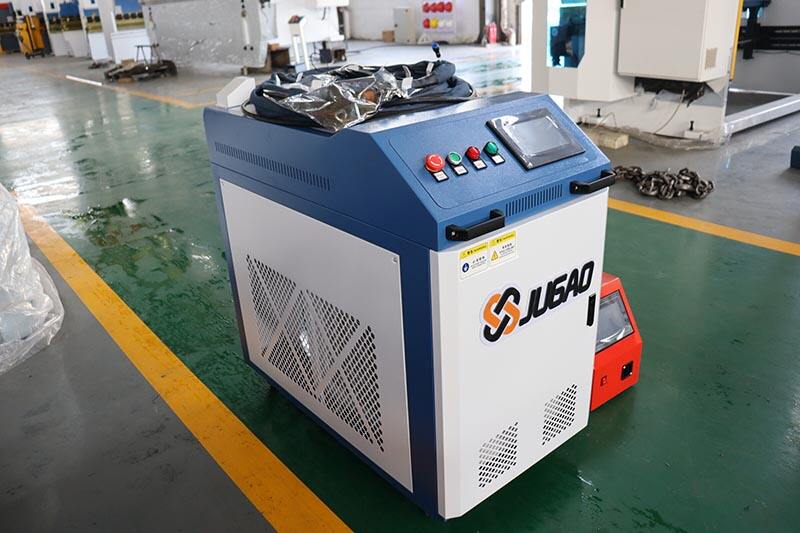

Application scenarios: Because the pulse laser rust removal machine can better control heat, it is suitable for application scenarios that require high-precision control of substrate temperature and protection of the substrate without damage, such as precision instrument rust removal. Due to its continuous beam characteristics, fiber laser is more suitable for rust removal of large steel components, pipes, rails and other large metal parts.

Advantages and Disadvantages: The advantages of pulsed lasers include long life, flexible output mode, high stability, easy maintenance, small heat-affected zone, and high coupling efficiency with metals. However,its photoelectric conversion efficiency is relatively low,and there are issues with internal temperature gradients that may cause thermal stress and thermal lensing. The advantages of fiber lasers include good beam quality and high efficiency, but the disadvantage is that the cost is relatively high and not suitable for applications such as precision rust removal that require higher precision control.

To sum up, pulse laser rust remover and fiber laser each have their own applicable scenarios, advantages and disadvantages, and the selection needs to be based on specific application requirements and cost considerations.