Press brake bending angle calculation method

The calculation of the bending angle of a CNC bending machine usually
involves multiple factors, including material type, plate thickness, bending
radius and bending coefficient. Different bending angles and material types
require different calculation methods and coefficients. The following are
methods for calculating bending angles for different types of materials:
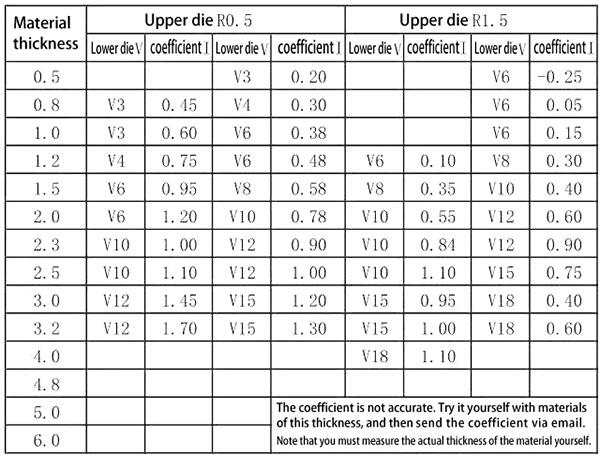
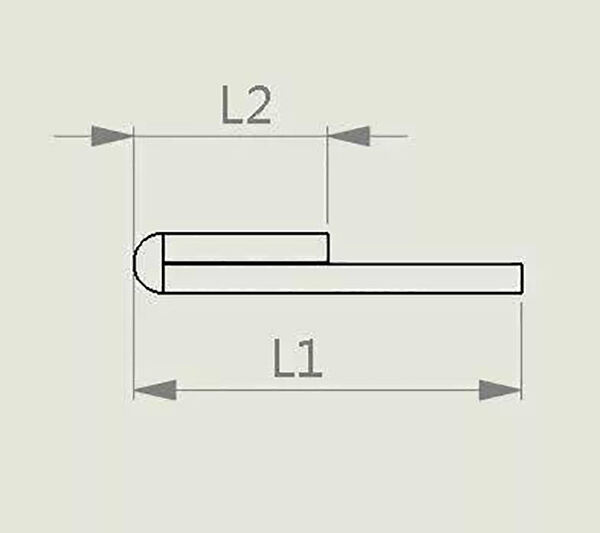
1. Iron plate bending: When bending at 90 degrees, the commonly used upper mold R is 0.5, the lower mold V is 5T, and the bending coefficient is 0.4T. The formula for calculating the expanded size is L1+L2-2T+coefficient.
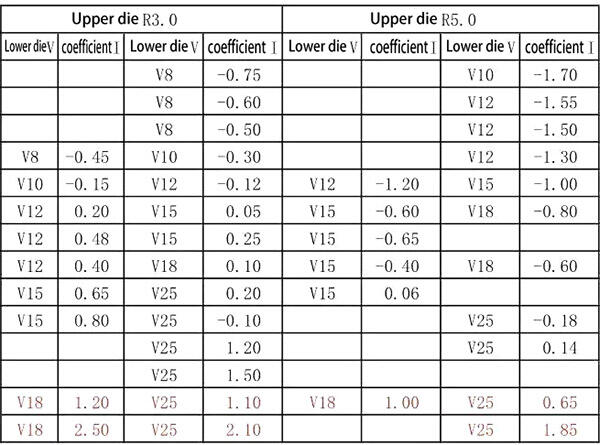
2. 60 degree bending of iron plate (using deep insertion die)
Expanded size=L1+L2+coefficient
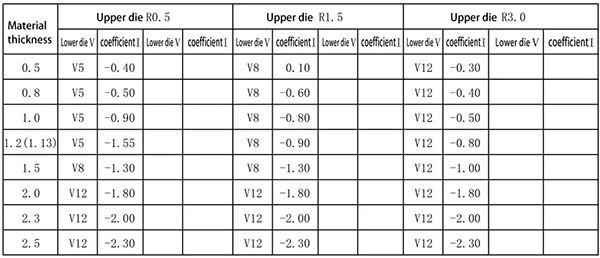
3. 30-degree bending of iron plate (use deep insertion die)
Expanded size=L1+L2+coefficient
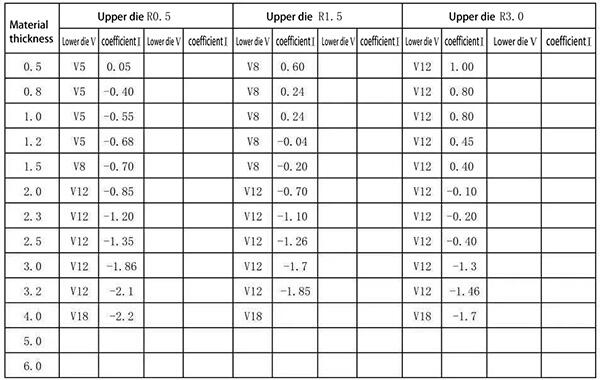
4.90-degree bending of aluminum plate: Normal bending upper die R0.5, lower die V=5T, bending coefficient 0.4T, V groove selection V=5T+R (R>0.5)
Expanded size=L1+L2-2T+coefficient
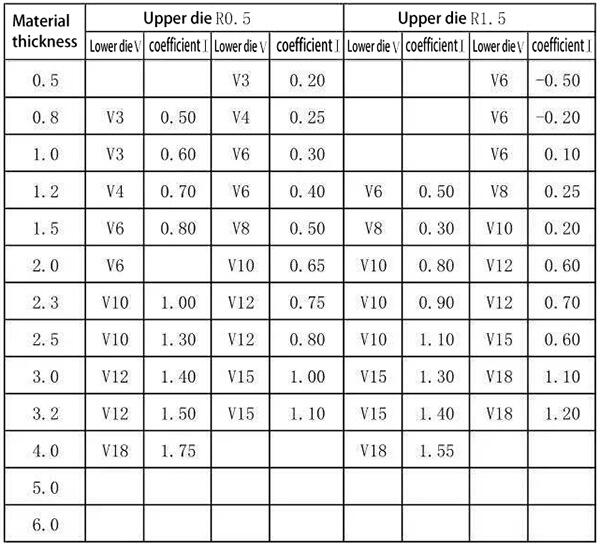
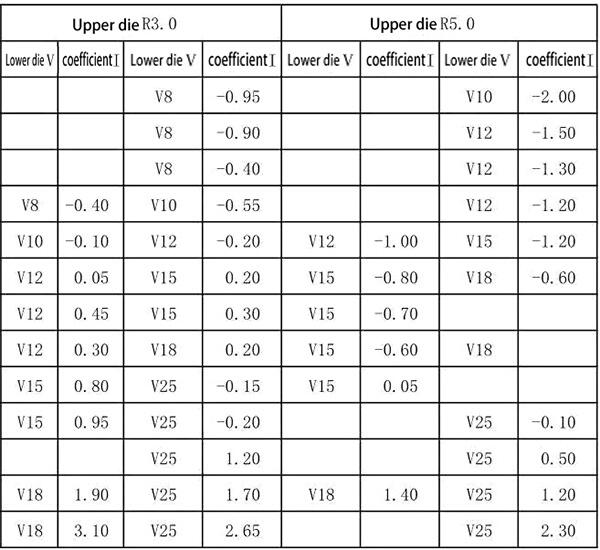
5.60 degree bending of aluminum plate (using deep insertion die)
Expanded size=L1+L2+coefficient
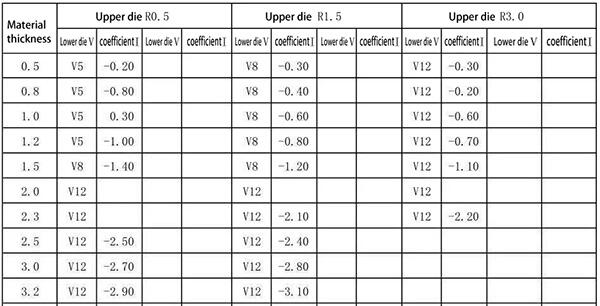
6.30-degree bending of aluminum plate (using deep insertion die)
Expanded size=L1+L2+coefficient
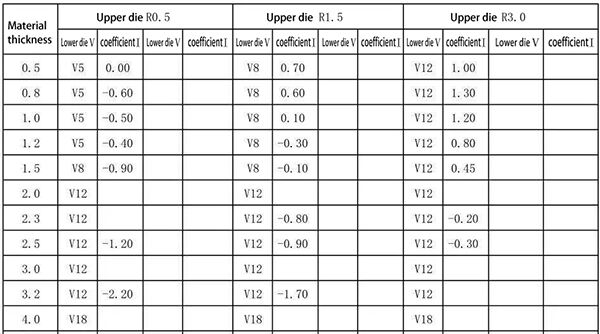
7. Dead edge coefficient (first use the deep-insertion die to fold a small angle, then use the flattening die to press the dead edge)
Above: Expanded size = L1+L2-0.55T
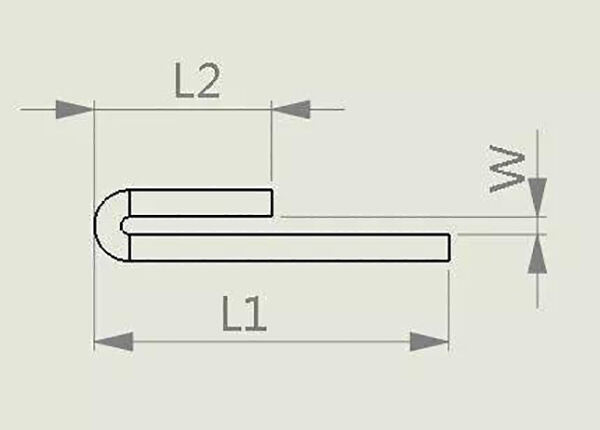
Above: Expanded size=L1+L2-0.55T+0.7W (W≤T)
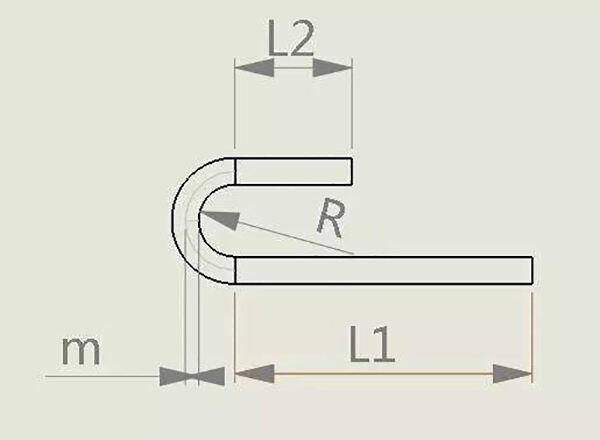
Above: Expanded size = L1+L2+3.14* (R+m) (2R>T)
T≤2.0,m=0.4T;
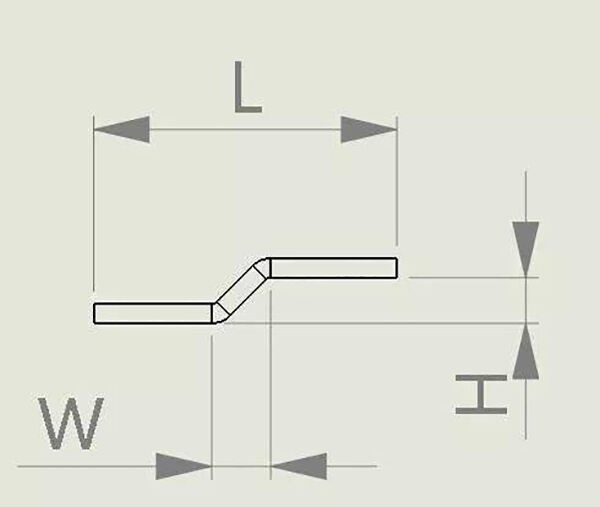
2.0 8. Pressure step difference coefficient A. When W ≥ 2T: the expansion is calculated as two single folds; B. When W<2T and H≥2T: the expansion is calculated as two single
folds; C. When W<2T, H<2T: expansion size = L+(H-T)*0.7; D. When W<2T, H=T: expanded size = L+0.15T; In addition, the calculation of the bending angle also involves the
relationship between the position of the neutral layer of the material and the
degree of deformation. In actual operation, it is very important to choose the
appropriate calculation formula and coefficient according to the specific
material, plate thickness and required bending angle.